9 Supplementary Information
9.1 File Formats
Where can you source reference genomes and annotation files:
- Ensembl database: https://asia.ensembl.org/info/data/ftp/index.html
- USCS database: https://hgdownload.soe.ucsc.edu/downloads.html
- NCBI database: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/guide/howto/dwn-genome/
The top of an ensembl homo sapiens fasta file:

Fasta files will have a chromosome header line, indicated by the line starting with >. The header line will have the chromosome number and may contain some extra information. A minimal header can just have the chromosome number.

The lines following the header will contain that specific chromosome’s sequence

Annotation files are usually GTF or GFF3 format files. Below is a GTF file:
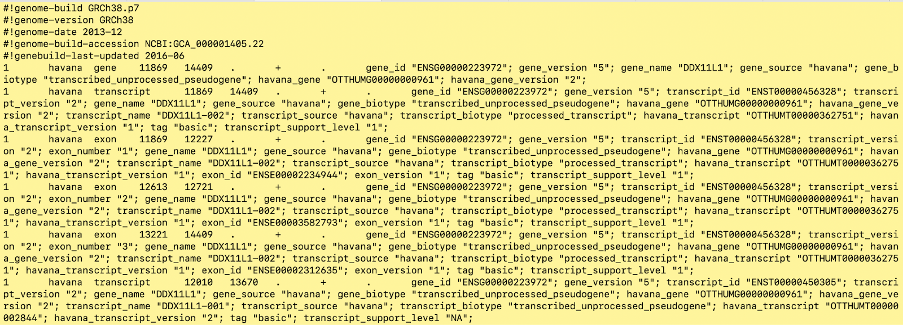
A gtf file is a ‘tab separated file’ - this means that it is a file with columns indicated by tab spacing. A GTF file will always have 9 columns containing the following information (taken from here):
- seqname - name of the chromosome or scaffold; chromosome names can be given with or without the ‘chr’ prefix. Note: the chromosome name format should be the same as the fasta file e.g if the fasta file has
chr1then the gtf file should also havechr1in this column. If the fasta file has1then the gtf file should have1in this column. - source - name of the program that generated this feature, or the data source (database or project name)
- feature - feature type name, e.g. Gene, Variation, Similarity
- start - Start position* of the feature, with sequence numbering starting at 1.
- end - End position* of the feature, with sequence numbering starting at 1.
- score - A floating point value.
- strand - defined as + (forward) or - (reverse).
- frame - One of ‘0’, ‘1’ or ‘2’. ‘0’ indicates that the first base of the feature is the first base of a codon, ‘1’ that the second base is the first base of a codon, and so on..
- attribute - A semicolon-separated list of tag-value pairs, providing additional information about each feature.